Reading Time: 4 minutes
Gallbladder Stones (Gallstones): Types, Risk Factors & Diet for Prevention.
The gallbladder, a pear-shaped organ nestled beneath your liver, plays a vital role in digestion by storing and concentrating bile.
However, sometimes unwanted guests can form within this storage unit – gallstones. These hard deposits can cause significant discomfort and require medical attention.
Let’s delve into the world of gallstones, exploring their types, how they develop, and who’s most at risk for encountering them.
Types of Gallstones: Cholesterol vs. Pigment
There are two main types of gallstones:
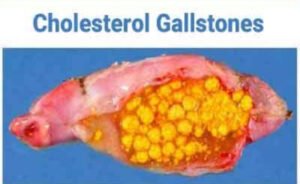
Cholesterol Gallstones:

These are the most common type, accounting for roughly 80% of cases. They form when cholesterol levels in bile become too high, or when bile doesn’t contain enough bile salts to keep cholesterol dissolved.
Pigment Gallstones:

These are less common, typically seen in individuals with chronic liver diseases or blood disorders that increase bilirubin levels in bile. Bilirubin, a waste product from red blood cell breakdown, can harden and form pigment gallstones.
From Liquid to Lumps: How Gallstones Develop
The formation of gallstones is a gradual process. Initially gallbladder sludge forms and persistent sludge transform into gallbladder stone when favourable conditions available for longer time. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
Supersaturation:
When cholesterol levels in bile become too high or there’s not enough bile salts, bile becomes supersaturated with cholesterol. Imagine a glass of water overflowing with sugar – it can’t hold any more.
Crystal Formation:
The excess cholesterol starts to come out of solution and forms tiny crystals.
Stone Growth:
Over time, these crystals can clump together and grow into gallstones. The size can vary from a grain of sand to a golf ball.
Who’s Likely to Get Invited to the Gallstone Party? Risk Factors

While anyone can develop gallstones, certain factors increase your risk:
Female Gender:
Women are two to three times more likely than men to develop gallstones, especially during pregnancy and hormonal fluctuations.
Age:
The risk of gallstones increases with age, particularly above 40.
Family History:
Having a close relative with gallstones increases your risk.
Obesity:
Excess weight is a significant risk factor, particularly in women.
Rapid Weight Loss:
Losing weight quickly can cause rapid changes in bile composition, increasing the risk of gallstone formation.
High-Cholesterol Diet:
A diet high in saturated fat and cholesterol can contribute to gallstone formation.
High-Triglyceride Levels:
Elevated levels of triglycerides in the blood can also increase the risk.
Certain Medical Conditions:
Conditions like cirrhosis, Crohn’s disease, and sickle cell anemia can increase the risk of gallstones.
Hormonal Therapy:
Estrogen-based medications like oral contraceptives can slightly elevate the risk of gallstones.
Dine Wise to Minimize Gallstone Woes:
A Dietary Guide for Gallbladder Health

The gallbladder, a small but mighty organ tucked under your liver, plays a crucial role in digestion by storing and concentrating bile.
However, unhealthy dietary habits can lead to the formation of gallstones, causing discomfort and potential health complications. But fear not, fellow foodies!
By making smart dietary choices, you can significantly reduce your risk of gallstone formation and keep your gallbladder happy.
Unveiling the Dietary Culprits: What to Limit
Certain dietary components can contribute to gallstone formation. Here’s what to keep an eye on:
Saturated Fats:
Excessive saturated fat intake, commonly found in fatty cuts of meat, processed foods, and fried items, can increase cholesterol levels in bile, promoting gallstone formation. Opt for lean protein sources, bake or grill instead of frying, and choose healthy fats like those found in olive oil and avocados.
Refined Carbohydrates:
Refined carbohydrates, like white bread, pasta, and sugary drinks, can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar. This can trigger the liver to produce more cholesterol, potentially leading to supersaturation of bile and gallstone formation. Choose whole grains over refined options, and limit sugary drinks.
High-Cholesterol Foods:
Foods high in cholesterol, such as organ meats, egg yolks (in moderation), and certain shellfish, can contribute to gallstone formation in individuals who are already predisposed. Opt for lean protein sources and limit these foods, especially if you have a family history of gallstones.
Dietary Champions for Gallbladder Health: Embrace These Foods
The good news is, there are plenty of dietary heroes that can support your gallbladder health:
Fiber-Rich Foods:
A diet rich in fiber, found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, helps regulate cholesterol levels and promotes healthy digestion. This can reduce the risk of gallstone formation. Aim for at least 25-35 grams of fiber daily.
Healthy Fats:
Including healthy fats from sources like olive oil, avocado, nuts, and seeds in your diet can help lower bad (LDL) cholesterol levels while increasing good (HDL) cholesterol. This can improve bile composition and reduce the risk of gallstones.
Fruits and Vegetables:
These colorful powerhouses are packed with antioxidants and essential nutrients that can promote overall health, including gallbladder health. Aim for a variety of fruits and vegetables throughout the day.
Calcium-Rich Foods:
Studies suggest that adequate calcium intake may contribute to preventing gallstones.Include low-fat dairy products, leafy greens, and calcium-fortified foods in your diet.
Conclusion: Knowledge is Power in Preventing Gallstones
Gallbladder Stones (Gallstones): Types, Risk Factors & Diet for Prevention. Understanding the types, formation process, and risk factors for gallstones empowers you to take preventative measures.
Maintaining a healthy weight, opting for a balanced diet low in saturated fats, and exercising regularly can significantly reduce your risk.
If you experience persistent upper right abdominal pain, especially after fatty meals, consult your doctor to rule out gallstones and discuss treatment options.
Remember, early detection and management can prevent complications and keep your digestive system running smoothly.