Reading Time: 6 minutes
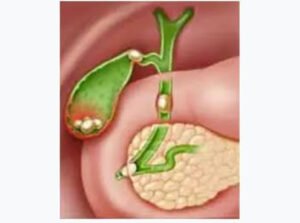
Gallbladder Stones: Symptoms, Complications & Diagnosis. The gallbladder, a pear-shaped organ nestled beneath your liver, plays a vital role in digestion by storing and concentrating bile. However, sometimes unwanted guests can form within this storage unit – gallstones.
These hardened deposits can cause significant discomfort and require medical attention.
While gallstones can sometimes be silent, with no noticeable symptoms, they can also cause a range of unpleasant experiences.
This article delves into the world of gallbladder stone symptoms, helping you recognize the signs complications, diagnosis and understand when to seek medical attention.
The Classic Sign: Gallbladder Attack (Biliary Colic) and Its Symptoms
The most common symptom associated with gallstones is a gallbladder attack (Biliary). This is a sudden and severe episode of pain in the upper right abdomen, typically lasting for 15 minutes to several hours.
The pain may be sharp, cramping, or a dull ache and can radiate to the back, right shoulder blade, or between the shoulder blades.
Here’s a closer look at some key symptoms associated with a gallbladder attack:

- Upper Right Abdominal Pain (Biliary Colic): This is the hallmark symptom and can be quite intense, often described as a squeezing or gnawing sensation.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms often accompany the abdominal pain and can worsen during an attack.
- Nausea Without Vomiting: Some individuals may experience nausea without vomiting throughout the attack.
- Bloating and Indigestion: Feeling full or bloated, along with indigestion and belching, can also occur during a gallbladder attack.
- Fever and Chills: In some cases, fever and chills may accompany the pain, especially if inflammation develops (cholecystitis).
Beyond the Attack: Other Potential Symptoms of Gallstones
While a gallbladder attack is the most prominent symptom, other signs may indicate gallstones, even in the absence of an attack. These may include:
Upper Right Abdominal Discomfort:
A dull or achy discomfort in the upper right abdomen, especially after eating fatty or greasy foods, can be a sign of gallstones.
Intolerance to Fatty Foods:
Fatty meals can trigger pain or indigestion in individuals with gallstones.
Chronic Indigestion:
Recurrent episodes of indigestion, heartburn, or belching can sometimes be linked to gallstones.
Complications of Untreated Gallbladder Stones: Risks You Shouldn’t Ignore.
Complications of untreated gallbladder stonescan be more than just a nagging discomfort.
They pose significant risks to your health and well-being.
10 Complications of Untreated Gallbladder Stones
Untreated gallbladder stones can lead to various complications, some of which can be severe and life-threatening. Here are 10 potential complications of untreated gallbladder stones:

Acute Cholecystitis:
Gallstones can block the cystic duct, causing inflammation of the gallbladder.
This condition, known as acute cholecystitis, is characterized by severe abdominal pain, fever, and potentially dangerous infections.
Gallbladder Perforation:
If acute cholecystitis is left untreated, it can lead to the rupture or perforation of the gallbladder.
This is a medical emergency that requires immediate surgery.
Empyema:
Untreated gallbladder infections can result in the accumulation of pus in the gallbladder, a condition called empyema.
It necessitates antibiotics and drainage, preferably surgery to remove the source of infection, that is the gallbladder in such condition.
Common Bile Duct Stones:
Gallstones can migrate from the gallbladder and become lodged in the common bile duct.
This can lead to jaundice, pancreatitis, and severe pain.
Cholangitis:
Obstructed bile ducts due to gallstones can cause cholangitis, a condition characterized by bile duct infection, fever, and abdominal pain.
Gallstone Ileus:
This rare but serious condition occurs when a large gallstone enters the small intestine after eroding gallbladder and adjacent small bowel ( duodenum) and moves down till lower part of small intestine and causes a bowel obstruction.
Gangrene of the Gallbladder:
Prolonged inflammation and blockage of the cystic duct can result in gangrene of the gallbladder, which is a life-threatening condition.
Acute Pancreatitis:
Gallstones blocking the pancreatic duct can trigger pancreatitis, leading to severe abdominal pain, digestive problems, and potentially organ damage.
Biliary Fistula:
In some cases, untreated gallbladder inflammation can result in the formation of an abnormal connection between the gallbladder and other organs, known as a biliary fistula.
Increased Risk of Gallbladder Cancer:
While rare, long-standing gallstones can elevate the risk of developing gallbladder cancer.
Given the potential severity of these complications, it’s crucial to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of gallbladder stones, such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or fever.
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help prevent these complications and ensure your overall health and well-being.
Diagnosis of Gallbladder Stones
While symptoms like gallbladder attacks can be a telltale sign, a definitive diagnosis is crucial for determining the best course of treatment. This article explores the various diagnostic tools available to identify gallstones with precision.
Ultrasound (USG): The First Line of Inquiry

Ultrasound is often the first line of investigation for suspected gallstones. This non-invasive and painless imaging technique uses sound waves to create a picture of the gallbladder and surrounding organs. Here’s what ultrasound can reveal:
- Presence of Gallstones: Ultrasound can effectively detect gallstones, appearing as bright echoes within the gallbladder.
- Size and Number of Gallstones: The size and number of gallstones can be visualized and measured with ultrasound.
- Thickening of the Gallbladder Wall: This finding can indicate inflammation (cholecystitis).
Despite its efficacy, ultrasound has limitations. It may not be as effective in individuals who are obese or have significant bowel gas, as these factors can obscure the image.
MRCP (Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography): A Deeper Look

Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is a non-invasive imaging technique that utilizes strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the bile ducts and pancreas. MRCP can be particularly helpful when:
- Ultrasound results are inconclusive.
- The doctor suspects a gallstone may be lodged in the bile duct.
- There’s a possibility of other conditions affecting the bile ducts or pancreas.
MRCP offers a clear visualization of the entire biliary system, including any blockages caused by gallstones. However, MRCP can be expensive and may not be readily available in all healthcare facilities.
CECT (Computed Tomography Enterography): A Multi-Faceted Approach
Computed tomography enterography (CECT) is a specialized CT scan that combines X-rays with a contrast dye to create detailed cross-sectional images of the abdomen and pelvis. CECT can be used to diagnose gallstones when:
- Other imaging tests are inconclusive.
- The doctor suspects complications of gallstones, such as inflammation or infection.
CECT provides a comprehensive view of the abdominal organs and can identify other potential causes of symptoms besides gallstones. However, CECT involves exposure to radiation, which may be a concern for some patients.
Blood Tests: Supporting the Diagnosis
While blood tests alone cannot definitively diagnose gallstones, they can be helpful in:
Identifying Inflammation:
Elevated levels of white blood cells or liver enzymes can suggest inflammation associated with gallstones (cholecystitis).
Assessing Liver Function:
Blood tests can evaluate liver function and identify potential complications of gallstones affecting the liver.
Blood tests play a supporting role in the diagnostic process, providing additional information alongside imaging studies.
Recognizing the Signs: When to Seek Medical Attention

If you experience any of the following symptoms, especially after a gallbladder attack, seek immediate medical attention:
- Intense and persistent pain in the upper right abdomen
- Pain radiating to the back, right shoulder blade, or between the shoulder blades
- Fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting that doesn’t subside
- Yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes (jaundice)
- Dark urine and pale stools
These symptoms may indicate complications arising from gallstones and require prompt medical evaluation and treatment.
Conclusion:
Understanding the symptoms of gallstones empowers you to recognize potential problems and seek medical attention promptly. While some individuals may have silent gallstones, for others, the signs can be quite clear.
By being aware of the classic symptoms like a gallbladder attack and other potential indicators, you can take charge of your health and ensure early intervention if needed.
Remember, a timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment can significantly improve your well-being and prevent complications.