कनकधारा स्तोत्र, धन प्राप्ति का चमत्कारी उपाय
Reading Time: 5 minutes Spread the love कनकधारा स्तोत्र, धन प्राप्ति का चमत्कारी उपाय धन की तलाश में हम सभी अपने जीवन में एक समय…
Dr AvinashTank, is a super-specialist (MCh) Laparoscopic Gastro-intestinal Surgeon,
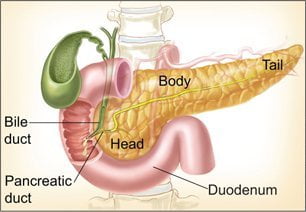
The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It’s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your liver, intestine, and other organs surround your pancreas.
The widest part of the pancreas is called the head. The head of the pancreas is closest to the small intestine. The middle section is called the body, and the thinnest part is called the tail.
The pancreas makes pancreatic juices. These juices contain enzymes that help break down food. The juices flow through a system of ducts leading to the main pancreatic duct. The pancreatic juices flow through the main duct to the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine.
The pancreas is also a gland that makes insulin and other hormones. These hormones enter the bloodstream and travel throughout the body. They help the body use or store the energy that comes from food. For example, insulin helps control the amount of sugar in the blood.
Cancer Cells
Cancer begins in cells, the building blocks that make up tissues. Tissues make up the pancreas and the other organs of the body.
Normal cells grow and divide to form new cells as the body needs them. When normal cells grow old or get damaged, they die, and new cells take their place.
Sometimes, this process goes wrong. New cells form when the body doesn’t need them, and old or damaged cells don’t die as they should. The buildup of extra cells often forms a mass of tissue called a growth or tumor.
Benign tumors (such as cysts):

Malignant growths:
Pancreatic cancer can invade other tissues, shed cancer cells into the abdomen, or spread to other organs:
When you get a diagnosis of cancer, it’s natural to wonder what may have caused the disease. Doctors can’t always explain why one person gets pancreatic cancer and another doesn’t. However, we do know that people with certain risk factors may be more likely than others to develop cancer of the pancreas. A risk factor is something that may increase the chance of getting a disease.
Studies have found the following risk factors for cancer of the pancreas:
Smoking: Smoking tobacco is the most important risk factor for pancreatic cancer. People who smoke tobacco are more likely than nonsmokers to develop this disease. Heavy smokers are most at risk.
Diabetes: People with diabetes are more likely than other people to develop pancreatic cancer.
Family history: Having a mother, father, sister, or brother with pancreatic cancer increases the risk of developing the disease.
Inflammation of the pancreas: Pancreatitis is a painful inflammation of the pancreas. Having pancreatitis for a long time may increase the risk of pancreatic cancer.
Obesity: People who are overweight or obese are slightly more likely than other people to develop pancreatic cancer.
Many other possible risk factors are under active study. For example, researchers are studying whether a diet high in fat (especially animal fat) or heavy drinking of alcoholic beverages may increase the risk of pancreatic cancer. Another area of active research is whether certain genes increase the risk of disease.
Many people who get pancreatic cancer have none of these risk factors, and many people who have known risk factors don’t develop the disease.
Early cancer of the pancreas often doesn’t cause symptoms. When the cancer grows larger, you may notice one or more of these common symptoms:
Also, advanced cancer may cause these general symptoms:
These symptoms may be caused by pancreatic cancer or by other health problems. People with these symptoms should tell their doctor so that problems can be diagnosed and treated as early as possible.
If you have symptoms that suggest cancer of the pancreas, your doctor will try to find out what’s causing the problems.
You may have blood or other lab tests. Also, you may have one or more of the following tests:
After extrahepatic bile duct cancer has been diagnosed, tests are done to find out if cancer cells have spread within the bile duct or to other parts of the body. The process used to find out if cancer has spread within the extrahepatic bile duct or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment.
Extrahepatic bile duct cancer may be staged following a laparotomy. A surgical incision is made in the wall of the abdomen to check the inside of the abdomen for signs of disease and to remove tissue andfluid for examination under a microscope. The results of the diagnostic imaging tests, laparotomy, andbiopsy are viewed together to determine the stage of the cancer. Sometimes, a laparoscopy will be done before the laparotomy to see if the cancer has spread. If the cancer has spread and cannot be removed by surgery, the surgeon may decide not to do a laparotomy.
There are three ways that cancer spreads in the body.
The three ways that cancer spreads in the body are:
When cancer cells break away from the primary (original) tumor and travel through the lymph or blood to other places in the body, another (secondary) tumor may form. This process is called metastasis. The secondary (metastatic) tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, ifbreast cancer spreads to the bones, the cancer cells in the bones are actually breast cancer cells. The disease is metastatic breast cancer, not bone cancer.
There are two staging systems for extrahepatic bile duct cancer.
Extrahepatic bile duct cancer has two staging systems. The staging system used depends on where in the extrahepatic bile duct the cancer first formed.
The following stages are used for perihilar extrahepatic bile duct cancer:
Stage 0 (Carcinoma in Situ)
In stage 0, abnormal cells are found in the innermost layer of tissue lining the perihilar bile duct. These abnormal cells may become cancer and spread into nearby normal tissue. Stage 0 is also called carcinoma in situ.
Stage I
In stage I, cancer has formed in the innermost layer of the wall of the perihilar bile duct and has spread into the muscle and fibrous tissue of the wall.
Stage II
In stage II, cancer has spread through the wall of the perihilar bile duct to nearby fatty tissue or to theliver.
Stage III
Stage III is divided into stages IIIA and IIIB.
Stage IV
Stage IV is divided into stages IVA and IVB.
The following stages are used for distal extrahepatic bile duct cancer:
Stage 0 (Carcinoma in Situ)
In stage 0, abnormal cells are found in the innermost layer of tissue lining the distal bile duct. These abnormal cells may become cancer and spread into nearby normal tissue. Stage 0 is also called carcinoma in situ.
Stage I
In stage I, cancer has formed. Stage I is divided into stages IA and IB.
Stage II
Stage II is divided into stages IIA and IIB.
Stage III
Stage IV
Depending on your cancer type and stage, our goals for treatment are:
Cure : This is the most important goal of cancer surgery. In fact as a cancer patient you are also strongly willing to have cure of cancer for forever. For most of the Liver & Gastro-intestinal cancers perhaps surgery is the first step for cure. Radiation &/or Chemotheray may be advised as an additional tool to achieve this goal.
Control : If your cancer is at a later stage or if previous treatments have been unsuccessful, we aim to control your cancer by removing as much as safely possible. Once you recover from surgery, radiation or chemotherapy is advised as important tool to control your cancer.
Comfort : If you have an advanced stage of cancer or one that hasn't responded to treatments and having symptoms because of tumor i.e pain, jaundice, vomiting, bleeding either in vomitus or in stool, then our multi-specialist team work together to sure you are free of pain and other symptoms.
Role of Surgery for Cancer treatment
Surgery can be done for many reasons for treatment of cancer.
Curative Surgery
Curative surgery is done when cancer is found in only one area, and it’s likely that all of the cancer can be removed. In this case, curative surgery can be the main treatment. It may be used alone or along with chemotherapy or radiation therapy, which can be given before or after the operation.
Diagnostic & Staging Surgery
This type of surgery is used to take out a piece of tissue (biopsy) to find out if cancer is present or what type of cancer it is. The diagnosis of cancer is made by looking at the cells under a microscope. Staging surgery is done to find out how much cancer there is and how far it has spread. The physical exam and the results of lab and imaging tests are used to figure out the clinical stage of the cancer. But the surgical stage (also called the pathologic stage) is usually a more exact measure of how far the cancer has spread. Examples of surgical procedures commonly used to stage cancers, like laparoscopy or laparotomy.
Palliative Surgery
This type of surgery is used to treat problems caused by advanced cancer. It is not done to cure the cancer. For example, cancers of intestine may grow large enough to block off (obstruct) the intestine, or tumor is bleeding and unable to control bleed by medical/endoscopic technique. If this happens, surgery can be used to remove the blockage/control bleeding.
Approach for Surgery:
How surgery is performed? (Special surgery techniques): Open Or Laparoscopic
Open Surgery:
It is the Gold Standard approach for Liver & Gastro-Intestinal cancer. An incision is given on the belly depending upton the underlying location of tumor so that surgeon can directly approach the cancer on cutting the belly. Open Surgery help to remove tumor safely if its adherent to near by blood vessels or organ, that is otherwise difficult in laparoscopic surgery.
Laparoscopic Surgery
A laparoscope is a long, thin, flexible tube that can be put through a small cut (incision) to look inside the body. In recent years, doctors have found that by creating small holes and using special instruments, the laparoscope can be used to perform surgery without making a large cut. This can help reduce blood loss during surgery and pain afterward. It can also shorten hospital stays and allow people to heal faster.
The role of laparoscopic surgery in cancer treatment is not yet clear. Doctors are now studying whether it is safe and effective to use laparoscopic surgeries for cancers of the stomach, colon, rectum & liver. It may prove to be as safe and work as well as standard surgery while cutting less and causing less damage to healthy tissues (being less invasive).
Biopsy of Cancer before Surgery
Biopsy is procedure to confirm the presence of cancer. It’s not essential before surgery. Usually biopsy is performed when 1. Suspicion is cause other than cancer, 2. When surgery cannot be done for cancer due to advanced stage of cancer or 3. Patient is unfit to undergo surgery. In these situation, biopsy guides for further therapy.
If all investigations suggest that cancer can be removed in totality from body, then biopsy can be avoided in to minimize the risk of spillage of cancer cell during biopsy procedure.
There is variety of way to perform biopsies:
Fine Needle Aspiration (FAN) biopsy
Fine needle aspiration (FNA) uses a very thin needle attached to a syringe to pull out small bits of tissue. The needle is guided into the tumor by looking at it using an imaging test, like an ultrasound or CT scan.
The main advantage of FNA is that there is no need to cut through the skin, so there is no surgical incision.
A drawback is that in some cases the needle can’t take out enough tissue for an exact diagnosis. A more invasive type of biopsy (one that involves larger needles or a cut in the skin) may then be needed.
Core Needle biopsy
This type of biopsy uses a larger needle to take out a core of tissue and done under guidance of imaging test like an ultrasound or CT scan. The advantage of core biopsy is that it usually collects enough tissue to find out whether the tumor is cancer.
Excisional or Incisional biopsy
For these biopsies, the surgeon remove the entire tumor (excisional biopsy) or a small part of the tumor (incisional biopsy).
Goal of liver cancer surgery
Depending on your cancer type and stage, our goals for treatment are:
Cure : This is the most important goal of cancer surgery. In fact as a cancer patient you are also strongly willing to have cure of cancer for forever. For most of the Liver & Gastro-intestinal cancers perhaps surgery is the first step for cure. Radiation &/or Chemotheray may be advised as an additional tool to achieve this goal.
Control : If your cancer is at a later stage or if previous treatments have been unsuccessful, we aim to control your cancer by removing as much as safely possible. Once you recover from surgery, radiation or chemotherapy is advised as important tool to control your cancer.
Comfort : If you have an advanced stage of cancer or one that hasn't responded to treatments and having symptoms because of tumor i.e pain, jaundice, vomiting, bleeding either in vomitus or in stool, then our multi-specialist team work together to sure you are free of pain and other symptoms.
Role of Surgery for liver Cancer treatment
Surgery can be done for many reasons for treatment of cancer.
Curative Surgery
Curative surgery is done when cancer is found in only one area, and it’s likely that all of the cancer can be removed. In this case, curative surgery can be the main treatment. It may be used alone or along with chemotherapy or radiation therapy, which can be given before or after the operation.
Diagnostic & Staging Surgery
This type of surgery is used to take out a piece of tissue (biopsy) to find out if cancer is present or what type of cancer it is. The diagnosis of cancer is made by looking at the cells under a microscope. Staging surgery is done to find out how much cancer there is and how far it has spread. The physical exam and the results of lab and imaging tests are used to figure out the clinical stage of the cancer. But the surgical stage (also called the pathologic stage) is usually a more exact measure of how far the cancer has spread. Examples of surgical procedures commonly used to stage cancers, like laparoscopy or laparotomy.
Palliative Surgery
This type of surgery is used to treat problems caused by advanced cancer. It is not done to cure the cancer. For example, cancers of intestine may grow large enough to block off (obstruct) the intestine, or tumor is bleeding and unable to control bleed by medical/endoscopic technique. If this happens, surgery can be used to remove the blockage/control bleeding.
Approach for Surgery:
How surgery is performed? (Special surgery techniques): Open Or Laparoscopic
Open Surgery:
It is the Gold Standard approach for Liver & Gastro-Intestinal cancer. An incision is given on the belly depending upton the underlying location of tumor so that surgeon can directly approach the cancer on cutting the belly. Open Surgery help to remove tumor safely if its adherent to near by blood vessels or organ, that is otherwise difficult in laparoscopic surgery.
Laparoscopic Surgery
A laparoscope is a long, thin, flexible tube that can be put through a small cut (incision) to look inside the body. In recent years, doctors have found that by creating small holes and using special instruments, the laparoscope can be used to perform surgery without making a large cut. This can help reduce blood loss during surgery and pain afterward. It can also shorten hospital stays and allow people to heal faster.
The role of laparoscopic surgery in cancer treatment is not yet clear. Doctors are now studying whether it is safe and effective to use laparoscopic surgeries for cancers of the stomach, colon, rectum & liver. It may prove to be as safe and work as well as standard surgery while cutting less and causing less damage to healthy tissues (being less invasive).
Biopsy of Cancer before Surgery
Biopsy is procedure to confirm the presence of cancer. It’s not essential before surgery. Usually biopsy is performed when 1. Suspicion is cause other than cancer, 2. When surgery cannot be done for cancer due to advanced stage of cancer or 3. Patient is unfit to undergo surgery. In these situation, biopsy guides for further therapy.
If all investigations suggest that cancer can be removed in totality from body, then biopsy can be avoided in to minimize the risk of spillage of cancer cell during biopsy procedure.
There is variety of way to perform biopsies:
Our expert team members shall help you to prepare you for surgery. You are strongly advised to stop smoking, stop drinking alcohol, try to improve your diet, lose weight, or actively exercise before surgery.
in most cases, you will need some tests before your surgery. The tests routinely used include:
Our expert team of Anaesthetist will ask you questions pertaining to your health and to assess your fitness for surgery. You are requested to tell them in detail about your current and past medical ailments, allergic reactions you’ve had in the past and current medicines that you are taking like blood thinning medicine. This medicine should be stopped 1 week prior to surgery.
Informed consent is one of the most important parts of “getting ready for surgery”. It is a process during which you are told about all aspects of the treatment before you give your doctor written permission to do the surgery.
Depending on the type of operation you have, there may be things you need to do to be ready for surgery:
Anaesthesia is the use of drugs to make the body unable to feel pain for a period of time. General anaesthesia puts you into a deep sleep for the surgery. It is often started by having you breathe into a face mask or by putting a drug into a vein in your arm. Once you are asleep, an endotracheal or ET tube is put in your throat to make it easy for you to breathe. Your heart rate, breathing rate, and blood pressure (vital signs) will be closely watched during the surgery. A doctor watches you throughout the procedure and until you wake up. They also take out the ET tube when the operation is over. You will be taken to the recovery room to be watched closely while the effects of the drugs wear off. This may take hours. People waking up from general anaesthesia often feel "out of it" for some time. Things may seem hazy or dream-like for a while. Your throat may be sore for a while from the endotracheal (ET) tube.
Your recovery right after surgery depends on many factors, including your state of health before the operation and how extensive the operation was performed.
You may feel pain at the site of surgery. We aim to keep you pain free after surgery with the help of latest and most effective technique or analgesic (pain relieving medicine).
As you are remains in bed on day of surgery, circulation of blood in leg become sluggish that may increase possibility of thrombo-embolism. To minimise it, you will be wearing leg stocking/ pneumatic compression boot to improve your leg circulation thus minimising the risk of thrombolism.
You may not feel much like eating or drinking, but this is an important part of the recovery process. Our health care team may start you out with ice chips or clear liquids. The stomach and intestines (digestive tract) is one of the last parts of the body to recover from the drugs used during surgery. You will need to have signs of stomach and bowel activity before you will be allowed to eat. You will likely be on a clear liquid diet until this happens. Once it does, you may get to try solid foods.
Our health care team will try to have you move around as soon as possible after surgery. They may even have you out of bed and walking the same day. While this may be hard at first, it helps speed your recovery by getting your digestive tract moving. It also helps your circulation and helps prevent blood clots from forming in your legs.
Our team shall also encourage you to do deep breathing exercises. This helps fully inflate your lungs and reduces the risk of pneumonia. You are advised to take deep breaths and cough every hour to help prevent lung infections. You will use an incentive spirometer (a small device used in breathing exercises to prevent complications after major surgery) 10-15 times every hour.
Once you are eating and walking, all tube/drains placed during surgery are removed, and then you may be ready to go home. Before leaving for home our health care team shall give you detailed guidance regarding diet, activities, medications & further plan of treatment.
There are risks that go with any type of medical procedure and surgery is no longer an exception. Success of surgery depends upon 3 factors: type of disease/surgery, experience of surgeon and overall health of patients. What’s important is whether the expected benefits outweigh the possible risks.
Doctors have been performing surgeries for a very long time. Advances in surgical techniques and our understanding of how to prevent infections have made modern surgery safer and less likely to damage healthy tissues than it has ever been. Still, there’s always a degree of risk involved, no matter how small. Different procedures have different kinds of risks and side effects. Be sure to discuss the details of your case with our health care team, who can give you a better idea about what your actual risks are. During surgery, possible complications during surgery may be caused by the surgery itself, the drugs used (anesthesia), or an underlying disease. Generally speaking, the more complex the surgery is the greater the risk. Complications in major surgical procedures include:
Pain Control
Cancer of the pancreas and its treatment may lead to pain. Your doctor or a specialist in pain control can suggest ways to relieve or reduce pain. You may want to ask if your hospital has a palliative care team.
There are many ways to relieve or reduce pain:
Pain medicine: Your health care team can suggest medicines that will relieve pain. If you have constipation or other side effects from the medicine, your health care team will help you manage the problems.
Nerve block: The doctor may inject alcohol into the area around certain nerves in the abdomen to block the pain.
Blockage
If the tumor in the pancreas grows large enough to squeeze the common bile duct or block the duodenum, your health care team can suggest ways to help:
Surgery: The surgeon can create a bypass through the blocked bile duct or duodenum. A bypass allows fluids to flow through the digestive tract. It can help relieve jaundice and pain resulting from the blockage.
Stent: The doctor uses an endoscope to place a stent in the blocked area. A stent is a tiny plastic or metal mesh tube that helps keep the duct or duodenum open.
Your recovery right after surgery depends on many factors, including your state of health before the operation and how extensive the operation was performed.

Experience
Award & Presentations
Satisfied Families
Successful Surgeries

Endoscopy
Successful Treatment of Pancreas Cancer in 70 yr old Lady. Dr Avinash Tank. Dwarika Hospital
Dr Avinash Tank, Dwarika Hospital, Ahmedabad July 12, 2023 7:50 pm
Reading Time: 5 minutes Spread the love कनकधारा स्तोत्र, धन प्राप्ति का चमत्कारी उपाय धन की तलाश में हम सभी अपने जीवन में एक समय…
Reading Time: 2 minutes Spread the love Mucus Discharge from Rectum After Stoma Surgery: Normal or Concerning? If you’ve had ostomy surgery, either a loop ileostomy…
Reading Time: 2 minutes Spread the love National Doctors Day 2024: Celebrating Our Medical Heroes on 1st July. Every year on 1st July, we come together…